Small business inventory reporting for taxes is a crucial aspect of tax compliance. Understanding the requirements, methods, and implications of inventory reporting can help small businesses avoid costly errors and optimize their tax strategies. This comprehensive guide will delve into the complexities of inventory reporting, providing practical insights and best practices to ensure accurate and efficient reporting.
Inventory reporting for taxes involves recording the value and quantity of inventory on hand at the end of each tax period. This information is used to calculate the cost of goods sold, which is a key factor in determining taxable income.
Small businesses must comply with specific tax laws and regulations regarding inventory reporting, including the use of approved inventory valuation methods and the filing of specific tax forms.
Inventory Reporting Requirements
Small businesses are legally obligated to report inventory for tax purposes. This is because inventory is considered an asset, and businesses must track their assets to determine their taxable income.
The specific tax forms and schedules that require inventory reporting include:
- Schedule C (Form 1040), Profit or Loss from Business
- Schedule SE (Form 1040), Self-Employment Tax
- Form 1120, U.S. Corporation Income Tax Return
- Form 1120-S, U.S. Income Tax Return for an S Corporation
There are several common inventory reporting methods that small businesses can use, including:
- The specific identification method
- The first-in, first-out (FIFO) method
- The last-in, first-out (LIFO) method
- The weighted average cost method
Inventory Tracking Systems
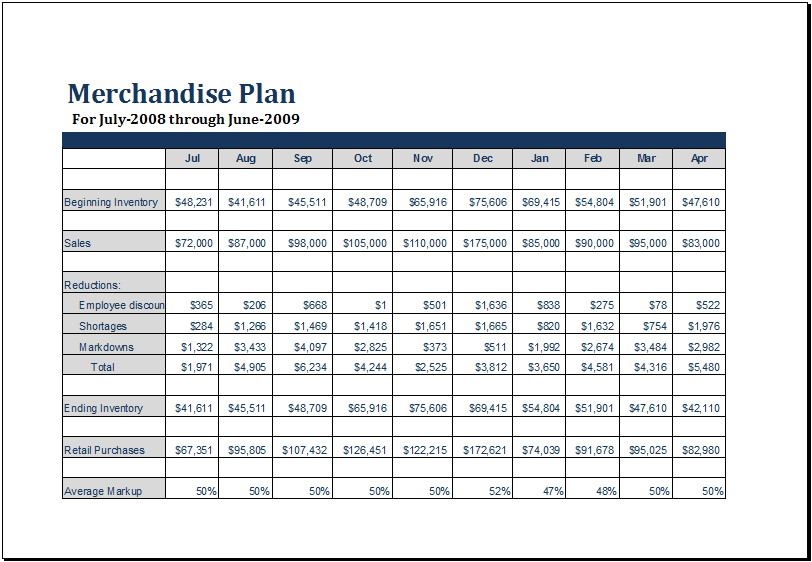
Inventory tracking is crucial for businesses to maintain accurate records, optimize stock levels, and prevent losses. Various methods exist to track inventory, each with its advantages and disadvantages. Understanding the different systems can help small businesses choose the most suitable option for their needs.
Manual Systems
Manual systems involve physically counting and recording inventory levels on paper or in spreadsheets. While simple and cost-effective, they can be prone to errors, especially with high-volume inventory or complex warehouses.
Spreadsheets
Spreadsheets offer a more structured approach than manual systems, allowing for digital data entry and manipulation. However, spreadsheets can still be susceptible to human error and may not provide real-time inventory visibility.
Inventory Management Software
Inventory management software is a comprehensive solution that automates inventory tracking, providing real-time visibility, inventory forecasting, and reporting capabilities. It can streamline inventory management, reduce errors, and improve efficiency.
Inventory Management Best Practices
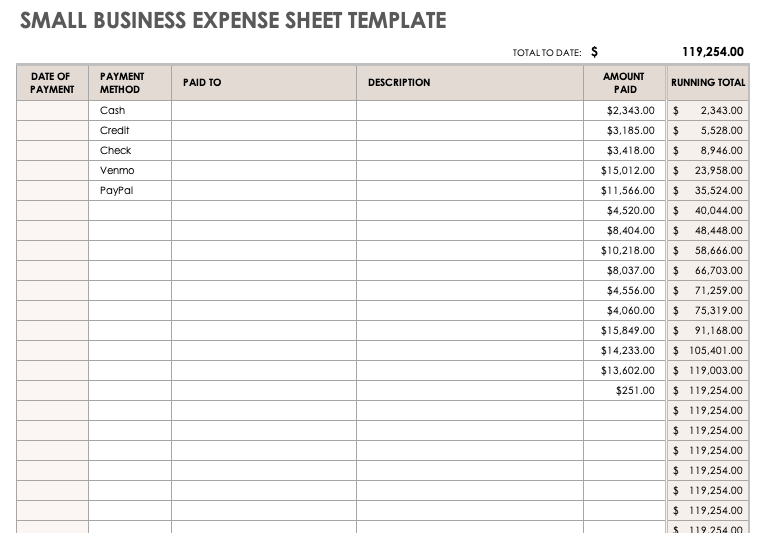
Effective inventory management is crucial for minimizing waste, optimizing stock levels, and reducing carrying costs. Implementing best practices ensures accurate inventory records, efficient operations, and improved profitability.
Inventory Management Techniques
Utilize techniques such as the First-In, First-Out (FIFO) or Last-In, First-Out (LIFO) methods to manage inventory flow. Consider implementing a perpetual inventory system for real-time updates on stock levels.
Regular Inventory Audits
Conduct regular inventory audits to verify physical inventory against records. This helps identify discrepancies, prevent shrinkage, and ensure accurate financial reporting.
Cycle Counts
Perform cycle counts by counting a portion of inventory regularly. This helps identify errors and variances, improving inventory accuracy and preventing large-scale discrepancies.
Reducing Inventory Carrying Costs
- Negotiate favorable terms with suppliers for discounts and extended payment periods.
- Implement just-in-time inventory management to minimize inventory holding costs.
- Consider consignment inventory arrangements to reduce carrying costs and increase flexibility.
Technology for Inventory Reporting: Small Business Inventory Reporting For Taxes
In the modern business landscape, technology plays a crucial role in streamlining inventory reporting and enhancing its efficiency. Cloud-based inventory management systems offer numerous advantages, simplifying the process and providing valuable insights.
Cloud-Based Inventory Management Systems
Cloud-based inventory management systems offer a range of benefits, including:
- Real-time inventory tracking, providing accurate and up-to-date information.
- Automated inventory updates, reducing the risk of errors and ensuring timely reporting.
- Centralized data storage, allowing for easy access and collaboration across multiple locations.
- Enhanced visibility and control over inventory levels, facilitating informed decision-making.
Specific Software Solutions
Several software solutions are available for small businesses, each offering unique features and capabilities. Some popular options include:
- QuickBooks Online:A comprehensive accounting and inventory management solution for small businesses.
- Zoho Inventory:A cloud-based inventory management system with robust features for tracking, forecasting, and reporting.
- Fishbowl:A feature-rich inventory management software designed for small and mid-sized businesses.
Common Inventory Reporting Errors
Accurate inventory reporting is crucial for businesses, as it impacts financial statements, tax calculations, and operational efficiency. However, several common errors can occur during inventory reporting, leading to inaccuracies and potential legal consequences.
To ensure accurate reporting, businesses must identify and address these errors proactively. Maintaining proper documentation and following best practices is essential for reliable inventory reporting.
Overstating Inventory
Overstating inventory refers to reporting a higher inventory value than what is physically available. This error can result in inflated asset values, overstated profits, and incorrect tax liability calculations.
Overstatement can occur due to several reasons, including:
- Inaccurate physical counts
- Unrecorded inventory write-offs
- Misidentified or obsolete inventory
Understating Inventory
Understating inventory is the opposite of overstating, where the reported inventory value is lower than the actual physical inventory. This error leads to understated assets, reduced profits, and potential tax underpayments.
Understatement can occur due to:
- Inaccurate physical counts
- Unrecorded inventory additions
- Mishandling of inventory shrinkage or spoilage
Inaccurate Inventory Valuation
Inaccurate inventory valuation occurs when the reported inventory value does not reflect the actual cost of the inventory. This error can arise due to:
- Using incorrect cost accounting methods
- Inconsistent application of inventory valuation policies
- Errors in recording inventory transactions
Lack of Documentation
Proper documentation is essential to support inventory reporting. Without adequate documentation, it becomes challenging to verify inventory counts, valuations, and transactions. This can lead to errors and increase the risk of fraud.
Consequences of Inventory Reporting Errors
Inventory reporting errors can have severe consequences for businesses, including:
- Inaccurate financial statements
- Overstated or understated tax liability
- Misleading financial performance indicators
- Increased risk of fraud
- Legal penalties
Tax Implications of Inventory Reporting
Inventory reporting is crucial for businesses to track their inventory accurately and ensure compliance with tax regulations. Understanding the tax implications of inventory reporting is essential for businesses to optimize their tax liability and avoid penalties.
Inventory reporting impacts both income taxes and sales taxes. For income tax purposes, the value of inventory is used to calculate cost of goods sold (COGS), which reduces taxable income. Businesses can use different inventory valuation methods, such as FIFO (first-in, first-out) or LIFO (last-in, first-out), which can affect the timing of COGS recognition and, therefore, the amount of income tax owed.
Sales Taxes
Inventory reporting also affects sales taxes. Businesses are generally required to pay sales tax on the sale of inventory. However, there may be exemptions or reduced rates for certain types of inventory, such as inventory sold for resale or inventory used in manufacturing.
Potential Tax Benefits
Optimizing inventory management can provide tax benefits for businesses. By reducing excess inventory and improving inventory turnover, businesses can lower their COGS and increase their taxable income. Additionally, businesses can take advantage of tax credits or deductions related to inventory management, such as the inventory tax credit or the deduction for inventory obsolescence.
Working with Tax Professionals, Small business inventory reporting for taxes
Businesses should work closely with tax professionals to ensure compliance with inventory reporting requirements and to optimize their tax liability. Tax professionals can provide guidance on inventory valuation methods, sales tax exemptions, and other tax-related matters.
Final Conclusion
By adhering to the principles Artikeld in this guide, small businesses can effectively manage their inventory and ensure accurate reporting for tax purposes. This not only helps them meet their tax obligations but also provides valuable insights into their inventory performance, enabling them to make informed decisions and optimize their operations for greater profitability.
Detailed FAQs
What are the legal obligations for small businesses regarding inventory reporting for taxes?
Small businesses are legally required to maintain accurate inventory records and report inventory values on their tax returns. Failure to comply can result in penalties and additional taxes.
What are the different inventory valuation methods available?
Common inventory valuation methods include FIFO (first-in, first-out), LIFO (last-in, first-out), and weighted average cost. Each method has its own advantages and disadvantages, and the most appropriate method for a specific business depends on its inventory turnover rate and tax implications.
What are the best practices for managing inventory effectively?
Best practices for inventory management include implementing a robust inventory tracking system, conducting regular inventory audits, and optimizing stock levels to minimize waste and carrying costs.
What are the tax implications of inventory reporting?
Inventory reporting can have significant tax implications, affecting income taxes and sales taxes. Understanding the tax laws and working with a tax professional can help businesses optimize their inventory management strategies for tax savings.
