Business inventory checklist – Embark on a journey to master business inventory management with our comprehensive checklist. This guide will equip you with the essential knowledge and practical steps to optimize your inventory, minimize costs, and enhance your business operations.
Effective inventory management is crucial for businesses of all sizes. It ensures you have the right products in stock to meet customer demand, optimizes cash flow, and prevents losses due to overstocking or understocking.
Inventory Management Basics
Inventory management is the process of overseeing the flow of goods from the moment they are acquired until they are sold to customers. It involves activities like forecasting demand, setting inventory levels, and managing stock levels to meet customer demand while minimizing costs.
Effective inventory management is crucial for businesses as it helps them avoid stockouts, reduce waste, and optimize cash flow. It also ensures that customers have access to the products they need, when they need them.
Tips for Effective Inventory Management
- Forecast demand accurately:This helps businesses determine the optimal inventory levels to meet customer demand without overstocking or understocking.
- Set appropriate inventory levels:Businesses need to find a balance between holding too much inventory (which can lead to waste and increased costs) and holding too little inventory (which can result in stockouts and lost sales).
- Manage stock levels effectively:This involves monitoring inventory levels, identifying slow-moving items, and implementing strategies to reduce excess inventory.
- Use inventory management software:This can help businesses automate inventory tracking, forecasting, and replenishment, improving efficiency and accuracy.
- Implement inventory control techniques:This includes cycle counting, periodic inventory audits, and regular inventory reconciliation to ensure accuracy and prevent shrinkage.
Creating a Business Inventory Checklist
A business inventory checklist is a comprehensive document that provides a detailed list of all the items that a business has in stock. It is an essential tool for managing inventory levels, ensuring that the business has the right amount of stock on hand to meet customer demand while minimizing waste and loss.
Creating an inventory checklist is a straightforward process that can be completed in a few simple steps:
Steps Involved in Creating an Inventory Checklist
- Identify the items to be included:Determine which items need to be tracked on the inventory checklist. This will typically include all items that are held in stock, such as raw materials, work-in-progress, and finished goods.
- Gather necessary information:For each item on the checklist, gather essential information such as the item’s name, description, SKU, quantity on hand, and reorder point.
- Organize the checklist:Group similar items together on the checklist to make it easier to manage and use. For example, all raw materials could be listed in one section, while all finished goods could be listed in another.
- Review and update regularly:The inventory checklist should be reviewed and updated regularly to ensure that it remains accurate and up-to-date. This will help to prevent errors and ensure that the business has a clear understanding of its inventory levels.
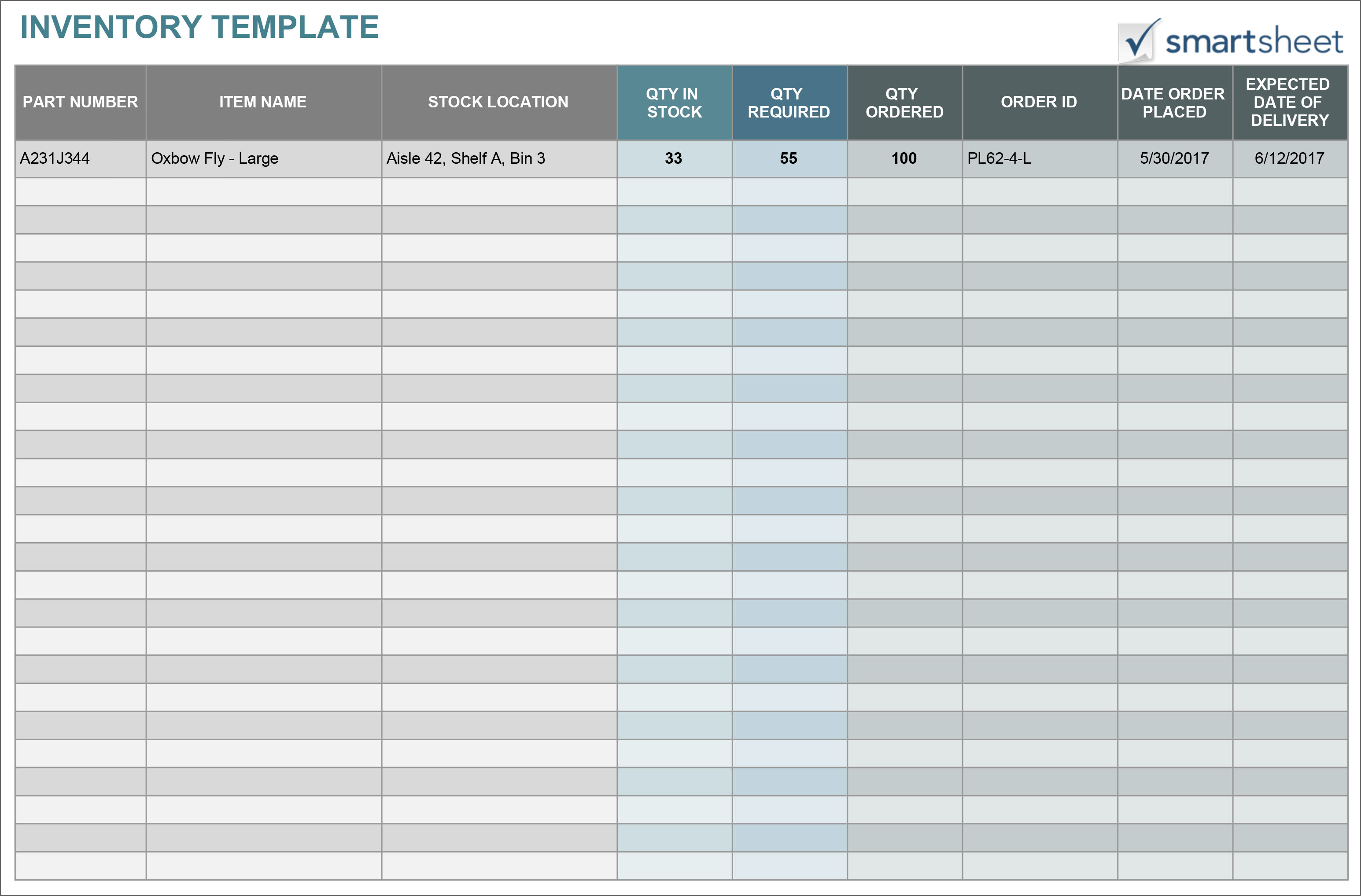
Essential Items to Include in an Inventory Checklist
The following are some essential items that should be included in a business inventory checklist:
- Item name
- Item description
- SKU (Stock Keeping Unit)
- Quantity on hand
- Reorder point
- Supplier information
- Item location
- Item condition
- Date of last inventory
Inventory Valuation Methods
Inventory valuation methods are accounting techniques used to determine the value of inventory on hand. The choice of valuation method can significantly impact a company’s financial statements and tax liability.
The most common inventory valuation methods are:
First-In, First-Out (FIFO)
FIFO assumes that the oldest inventory is sold first. This method results in a higher cost of goods sold (COGS) and lower ending inventory in periods of rising prices, and vice versa in periods of falling prices.
Advantages of FIFO
- Reflects the physical flow of inventory.
- Provides a more conservative estimate of COGS.
- Simplifies inventory tracking.
Disadvantages of FIFO
- May not reflect the current market value of inventory.
- Can result in large swings in COGS and ending inventory during periods of price fluctuations.
Last-In, First-Out (LIFO)
LIFO assumes that the most recently purchased inventory is sold first. This method results in a lower COGS and higher ending inventory in periods of rising prices, and vice versa in periods of falling prices.
Advantages of LIFO
- Reflects the current market value of inventory.
- Provides a more stable estimate of COGS.
- Can reduce taxable income in periods of rising prices.
Disadvantages of LIFO
- May not reflect the physical flow of inventory.
- Can result in negative inventory balances during periods of falling prices.
- Requires more complex inventory tracking.
Weighted Average
Weighted average assumes that all units of inventory are sold at an average cost. This method results in a COGS and ending inventory that is a blend of the costs of all units on hand.
Advantages of Weighted Average
- Provides a more accurate estimate of COGS and ending inventory.
- Simplifies inventory tracking.
- Avoids the extreme fluctuations in COGS and ending inventory that can occur with FIFO and LIFO.
Disadvantages of Weighted Average
- May not reflect the current market value of inventory.
- Can be more complex to calculate than FIFO or LIFO.
Choosing the Appropriate Valuation Method
The choice of inventory valuation method depends on several factors, including:
- The nature of the business.
- The rate of inventory turnover.
- The expected price fluctuations of inventory.
- The tax implications of the valuation method.
Companies should carefully consider these factors when selecting an inventory valuation method to ensure that it accurately reflects the value of their inventory and meets their financial reporting objectives.
Inventory Control Techniques
Inventory control techniques are strategies and methods businesses use to manage their inventory efficiently and effectively. These techniques aim to minimize waste, reduce costs, and optimize stock levels to meet customer demand.
Various inventory control techniques exist, each with its own benefits and challenges. Understanding these techniques can help businesses choose the most appropriate approach for their specific needs.
ABC Analysis
ABC analysis is a technique that classifies inventory items into three categories based on their value and importance: A, B, and C.
- A items: High-value items that account for a large portion of total inventory value. These items require close monitoring and tight control.
- B items: Medium-value items that require moderate control and monitoring.
- C items: Low-value items that account for a small portion of total inventory value. These items can be managed with less stringent controls.
ABC analysis helps businesses prioritize inventory management efforts and allocate resources accordingly.
Just-in-Time Inventory (JIT)
JIT inventory is a technique that aims to minimize inventory levels by receiving inventory only when it is needed for production or sale. This approach reduces holding costs, storage space requirements, and the risk of obsolescence.
- Benefits: Reduced inventory costs, improved cash flow, and increased flexibility.
- Challenges: Requires accurate demand forecasting, reliable suppliers, and efficient logistics.
JIT inventory is commonly used in manufacturing environments where production is closely aligned with customer demand.
Inventory Optimization Strategies
Inventory optimization is the process of managing inventory levels to ensure that a business has the right amount of inventory on hand to meet customer demand without incurring excessive carrying costs. Optimizing inventory levels can help businesses improve cash flow, reduce waste, and increase profitability.There are several strategies that businesses can use to optimize inventory levels.
One common strategy is to use the economic order quantity (EOQ) formula to determine the optimal order quantity for each item. The EOQ formula takes into account the following factors:
- Annual demand for the item
- Ordering cost per order
- Carrying cost per unit per year
Another common strategy is to use a safety stock level to ensure that the business has enough inventory on hand to meet unexpected demand. The safety stock level is typically set as a percentage of the average demand for the item.Businesses can also use technology to help them optimize inventory levels.
There are a number of software programs that can help businesses track inventory levels, forecast demand, and generate purchase orders. These programs can help businesses improve the accuracy of their inventory data and make better decisions about inventory levels.
Inventory Valuation Methods
There are a number of different inventory valuation methods that businesses can use. The most common inventory valuation methods are:
- First-in, first-out (FIFO)
- Last-in, first-out (LIFO)
- Weighted average cost
The FIFO method assumes that the first items purchased are the first items sold. The LIFO method assumes that the last items purchased are the first items sold. The weighted average cost method assumes that the cost of each item sold is the average cost of all items in inventory.The choice of inventory valuation method can have a significant impact on a business’s financial statements.
For example, if the cost of inventory is rising, the FIFO method will result in a higher cost of goods sold and a lower net income than the LIFO method.
Inventory Control Techniques
There are a number of different inventory control techniques that businesses can use to manage their inventory levels. Some common inventory control techniques include:
- Just-in-time (JIT) inventory
- Kanban inventory
- Vendor-managed inventory (VMI)
The JIT inventory system is a production system that minimizes inventory by producing only what is needed, when it is needed. The Kanban inventory system is a visual inventory control system that uses cards to track the flow of inventory.
The VMI system is an inventory management system in which the supplier manages the inventory levels for the customer.The choice of inventory control technique depends on a number of factors, such as the type of business, the size of the business, and the nature of the inventory.
Inventory Reporting and Analysis
Inventory reporting and analysis are crucial for businesses to gain insights into their inventory levels, identify trends, and make informed decisions. Through comprehensive reports, businesses can monitor their inventory performance, optimize stock levels, and minimize losses.
Types of Inventory Reports, Business inventory checklist
Businesses can generate various inventory reports to meet their specific needs, including:
- Stock Status Report: Provides a snapshot of current inventory levels, including quantity on hand, available stock, and committed stock.
- Inventory Valuation Report: Determines the total value of inventory based on different valuation methods, such as FIFO (First-In, First-Out) or LIFO (Last-In, First-Out).
- Inventory Turnover Report: Measures how quickly inventory is sold and replaced, indicating the efficiency of inventory management.
- Inventory Aging Report: Analyzes the age of inventory, highlighting slow-moving or obsolete items that need attention.
- Inventory Discrepancy Report: Identifies discrepancies between physical inventory counts and system records, indicating potential errors or theft.
Analyzing Inventory Reports
By analyzing inventory reports, businesses can identify trends and patterns in their inventory management practices. This analysis helps them:
- Forecast demand and optimize stock levels to avoid overstocking or stockouts.
- Identify slow-moving or obsolete items that can be discounted or removed from inventory.
- Monitor inventory turnover rates to ensure efficient stock replenishment and minimize carrying costs.
- Detect inventory discrepancies and implement measures to prevent losses due to theft or errors.
- Track inventory valuation and ensure accurate financial reporting.
Dashboards and Inventory Analysis Tools
Dashboards and other inventory analysis tools provide a visual representation of key inventory metrics, making it easier to monitor and analyze inventory performance. These tools can include:
- Inventory dashboards: Display real-time inventory data, including stock levels, turnover rates, and discrepancies.
- Inventory forecasting tools: Predict future demand based on historical data and market trends.
- Inventory optimization software: Provides recommendations for optimizing stock levels, reducing carrying costs, and improving inventory efficiency.
By utilizing inventory reporting and analysis, businesses can gain valuable insights into their inventory management practices, identify areas for improvement, and make informed decisions to optimize their inventory operations.
Wrap-Up
By implementing the strategies and techniques Artikeld in this checklist, you can establish a robust inventory management system that drives efficiency, profitability, and customer satisfaction. Remember, inventory management is an ongoing process that requires regular review and adjustment to align with evolving business needs and market trends.
Helpful Answers
What are the key elements of a business inventory checklist?
A comprehensive business inventory checklist should include details such as product name, description, quantity on hand, reorder point, safety stock level, unit cost, and total value.
How can I choose the appropriate inventory valuation method for my business?
Consider factors such as industry norms, tax implications, and the level of accuracy required when selecting an inventory valuation method. FIFO (First-In, First-Out), LIFO (Last-In, First-Out), and weighted average are common methods.
What are some effective inventory control techniques?
Implement techniques like ABC analysis to categorize inventory items based on their value and turnover, just-in-time inventory to minimize holding costs, and cycle counting to ensure inventory accuracy.
